Early stages of bladder cancer often have no symptoms. The bladder is made up of layers – the urothelium (lining), smooth muscle, and connective tissue. The most common type of bladder cancer, transitional or urothelial cell, starts in the lining (urothelium) of the bladder wall. If left untreated it may then invade into the muscle or fatty layers of the bladder and eventually spread to other areas. Your first warning sign may be blood in your urine, but sometimes that blood may only be visible under a microscope. So how do you catch bladder cancer in early stages?
Know if You Are at Higher Risk
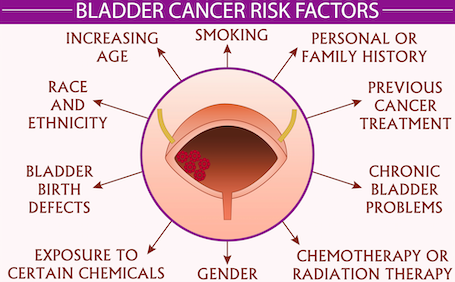
There are certain factors that increase your risk of bladder cancer. Knowing these risk factors can help you keep a closer eye on your health and make smarter decisions with your diet and other activities. The following factors increase your risk of bladder cancer:
Controllable Factors
Cigarette Smoking
This is by far the greatest risk factor. According to the American Cancer Society, smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers and people who smoke are at least three times as likely to get bladder cancer as people who don’t.
Workplace Exposure to Chemicals
People who work in industries that use certain organic chemicals may have a higher risk of bladder cancer. Higher-risk industries include printing companies, and manufacturers of rubber, leather, textiles, and paint products. Painters, machinists, printers, hairdressers (heavy exposure to hair dyes), and truck drivers (exposure to diesel fumes).
High-Fat Diet
People who eat a diet high in fat have a higher risk of developing bladder cancer.
The National Academy of Sciences, USA estimates that 60% of female cancers of all kinds and 40% of male cancers are related to nutritional factors [7,23,24]. Among two food sources in the human diet-plants and animal meats-it appears that plant-based diet is more health beneficial and could reduce cancer risk even by 30-40% [7,23, 25,26].
Chemotherapy or Radiation
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy for other cancers can increase the risk for other cancers.According to the Mayo Clinic, treatment with the anti-cancer drug cyclophosphamide increases the risk of bladder cancer. People who received radiation treatments aimed at the pelvis for a previous cancer have a higher risk of developing bladder cancer.
Uncontrollable Factors
Gender
Due to physiological differences, males are at much higher risk for bladder cancer.
Age
Age plays a role in your risk level as well. The average age someone is diagnosed with bladder cancer is 67.
Race
Caucasians are at higher risk than people of other races to get bladder cancer.
Medical History
If you have a family member who has or has had bladder cancer, you are at an increased risk for developing this disease. Family members with bladder cancer may have been exposed to the same carcinogen, or they may all have certain genetic abnormalities associated with bladder cancer. Therefore, both a family history or a personal history of bladder cancer increases your risk of developing it.
Chronic Bladder Inflammation
Chronic inflammation of the bladder can be caused by factors like ongoing infection, abnormal immune response, obesity, diet, lack of sleep, and too much stress. Over time it can damage cell DNA and affect the way cells grow and divide. That could lead to the growth of tumors and cancer.
Urinary Catheter Use
One of the most common and severe complications that occurs with urinary catheters is a UTI, referred to as a “catheter-associated urinary tract infection” or CAUTI.
Are You at High Risk for Bladder Cancer?
It’s important to know about the risk factors for bladder cancer because there may be things you can do that might lower your risk of getting it. If you’re at higher risk because of certain factors, you might be helped by tests that could find it early, when treatment is most likely to be effective. Some doctors may recommend bladder cancer screenings for people at very high risk. You may be considered high risk if:
- You’ve had bladder cancer before
- You have certain birth defects of the bladder
- You are or have been exposed to certain chemicals at work
Symptoms of Cancer in the Bladder
- Painful urination
- Frequent urination or feeling an urge to urinate without results
- Slow or intermittent urine stream
- Pelvic pain
- Back pain
While these symptoms could indicate bladder cancer, they are nonspecific and could also indicate other medical problems including urinary tract infections, bladder stones or prostate disorders. Get a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of the symptoms and to exclude bladder cancer.
We Offer Many Treatments for Bladder Cancer
At KCUC Urology & Oncology, with 31 of the finest urologists in the country, a team of radiation oncologists, a medical oncologist, pathologists and 14 non-physician providers, we are the premier urology and oncology group in Kansas City. We offer many treatments for bladder cancer.